Latest News
Indira Nehru Gandhi v. Shri Raj Narain & Anr., 1975
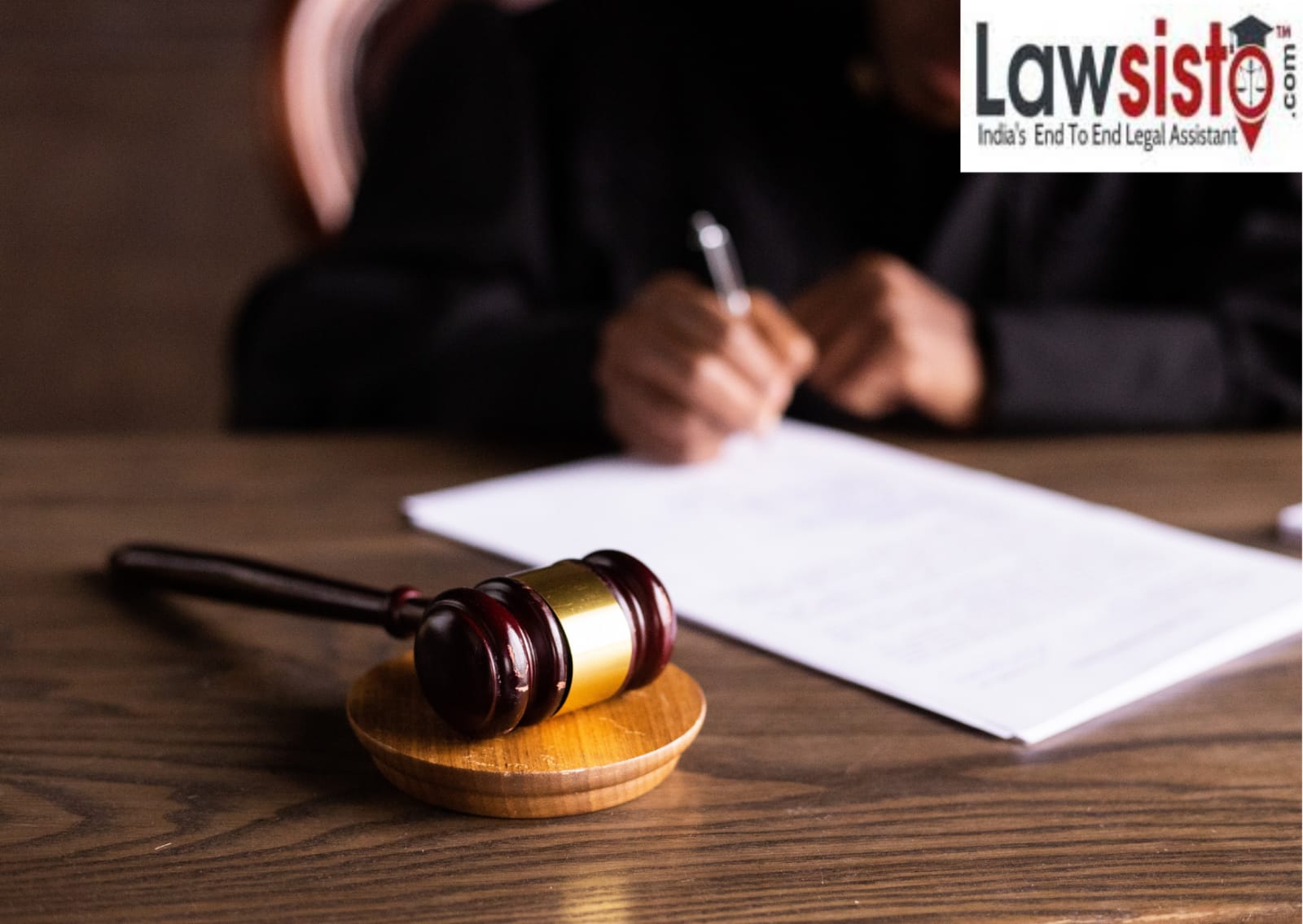
Introduction:
It was the landmark case that made history and prompted the burden of Emergency in India from 1975 to 1977. It is the case which scrutinized the forces of the legal executive, an exhibit of how Parliament anticipated that the legal executive should stoop down before them. Parliament attempted to set up its incomparability throughout this case however set up by the legal executive. This case addressed so numerous vital parts of the Constitution, for example, its Basic structure, intensity of locale of courts, division of three organs of the express that are: Legislative, leader and legal executive, elements of Legislature, the option to free and reasonable races, rule of law and legal audit and finally, political equity.
With the case destroying light on endless parts of law and political foundation of India, even a book was composed on it named as:
The case that Shook India by Prashant Bhushan, who was the child of the backer for the case and had immovably thought all aspects of the case. It was the first run through throughout the entire existence of India that appointment of a Prime Minister was saved. The case made an enormous hit to the tenet of the Basic Structure of the Constitution, which was held that it couldn't be corrected a couple of years earlier in the landmark judgment case of Keshvananda Bharti versus Union of India (1973). The becoming aware of the case in Supreme court occurred during the crisis during which the essential rights were suspended and press restriction was upheld, because of which there were no formal review or conceivable announcing of the case. The case was a major effect on Indian governmental issues.
Background:
In 1971, when the fifth Lok Sabha decisions were held, Indira Gandhi and her gathering arose successful, making sure about a sum of 352 seats out of 518 seats in the said races. She battled her political decision from the Rae Bareilly Constituency and against her challenging was Raj Narain, head of Ram Manohar Lohia's SSP. Despite the fact that he was sure of his victory against Mrs. Gandhi, he lost by an enormous edge.
Baffled with the thrashing, he recorded an appeal to invalidate the political race and blamed Indira Gandhi for utilizing degenerate practices in the political race to guarantee triumph. On 24th April 1971, he tested the Prime Minister's political decision by documenting a request in the Allahabad High Court and blamed Gandhi for abusing the political decision code in the Representation of the People Act, 1951. He communicated that her political races were helped by numerous Government authorities which were comprehensive of military and nearby police.
Aside from that, he claimed that Indira Gandhi has utilized Government vehicles for her political races, disseminated alcohol and covers to the citizens to impact them to decide in favour of her, surpassing the mission costs.
The Allahabad High court announced Indira Gandhi's political decision void on the grounds of degenerate practices on twelfth June 1975, the court, talking under Justice Jagmohanlal Sinha saw Indira Gandhi as liable of abusing Government apparatus u/s-123(7) of Representative of individuals' demonstration, 1951.[1]As an outcome, she was banished from challenging into races for an additional six years. Bothered by this choice, she advanced in Supreme Court, yet SC being in get-away by then, conceded an execution remains.
From there on, a highly sensitive situation was announced by the then President Fakhrudeen Ali Ahmad expressing that the purpose behind it was inner unsettling influences however it is obviously clear that the 'genuine explanation' that prompted crisis was the judgment of Allahabad High Court for the situation of Raj Narain versus Uttar Pradesh. And on tenth August 1975, 39th Constitutional (Amendment) Act, 1971 was passed by embeddings Article 329-An in the Constitution which by and large banned the locale of Supreme Court structure engaging the matter of races making the appointment of President, Prime Minister, Vice-President and the Speaker of Lok Sabha baseless in the court of law.
The Doctrine of Basic structure says that Parliament's boundless capacity to change the Constitution is dependent upon limitation, which implies it ought not to abuse the fundamental structure of the Constitution. This teaching was set down in the Keshvananda Bharti case. Article 368 of the Constitution offers the capacity to the Parliament to reexamine the Constitution by development, assortment or abrogation of any arrangement as demonstrated by the strategy set down in that. It was communicated that Clause(4) of Article 329-A should be struck down as it abused the norm of free and reasonable races which is an essential piece of the fundamental structure of the Constitution. It is seen that the best way to determine any question which emerges in a political race is by means of legal survey and article 329-A grabs away these rights from the court. Free and reasonable races are the vital highlights of a majority rule government and it is significant that if decisions are won by malignance, the legal executive needs to mediate to guarantee equity is served.
Judgment:
The court gave its judgment on seventh November 1975 and was the main case where the landmark choice of Kesvananda Bharti case was applied. The peak court maintained the conflict of the respondent and announced statement (4) of Article 329-An as illegal.
Mathew J said that Article 329-A(4) devastated the essential structure of the constitution. He was of the view that a 'sound vote based system' can possibly work when there is a probability of free and reasonable races and the reviled correction crushed that chance.
Chandrachud J. discovered that the revision was violative of the guideline of 'division of forces' as it wilfully moved a capacity under the control of the administration which was simply legal. He was likewise of the view that the correction is violative of Article 14 as it makes inconsistent places of explicit individuals from the Parliament against others.
Beam C.J held that one more essential component was disregarded by the said revision i.e the standard of law and Justice Khanna was of the assessment of infringement of standards of free and reasonable rates.
The seat likewise held that the correction was violative of the standards of normal equity i.e Audi Alterum Partemwhich signifies 'tuning in to the opposite side' as it was denying the option to reasonable knowledge about the individuals who were testing the appointment of the individuals referenced in the Amendment.
Thus it was on shifted reasons that the 39th Amendment act, 1975 was struck down as it was illegal and violative of the essential structure of the Constitution.
Conclusion:
The court demonstrated that the Parliament is by Law and its not the other way around. Legal executive squashed the Parliament's course to set up incomparability and the endeavour to make itself over the Constitution. The Court upheld the embodiment of popular government i.e free and reasonable rates. In the essence of the substance, the principle point of the Amendment was to invert the High Court's judgment that discredited Indira Gandhi's political race. What's more, rather than leaving, she forced crisis and passed the draconian 39th Amendment Act,1975 which was stuck somewhere around the Supreme Court. The case maintained both Rule of Law and Separation of Power and made it totally evident that approval or nullification of races is without a doubt a legal issue and can't be meddled by the Legislature. Assume control over maintained majority rules system. Indira Gandhi's noxious endeavours of placing her Government's authoritative forces over the Constitution came all smashing down and the Fundamental Rights Case choice end up being exact and exact to its centre.
Document: