Latest News
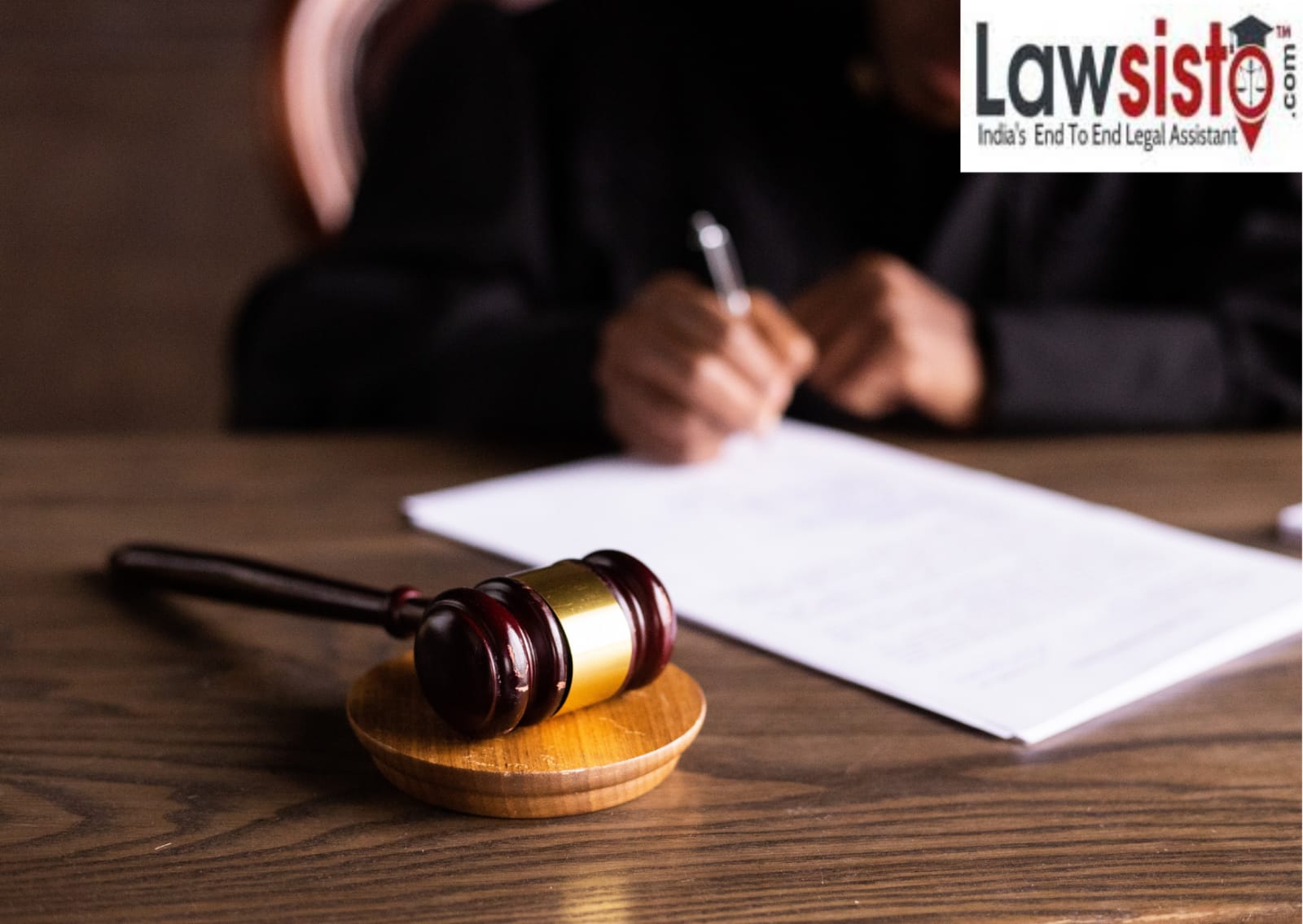
Delhi High Court rejects Punjab National Bank's plea under Section 482 CrPc against RBI

The Delhi High Court on Friday disregarded the petitions filed with the aid of using Punjab National Bank (PNB) and its past due to worker, IP Singh, looking for to quash the order of issuance of the system below Section 482 of the Criminal Procedure Code [Punjab National Bank Vs. NCT of Delhi & Another] Justice Anu Malhotra of the Delhi High Court disregarded the 2 petitions filed with the aid of using PNB and it is a former worker below Section 482 of the CrPC.
The petitions had been filed looking to set apart a Patiala House District Court order from March 11, 2019, that summoned the Punjab National Bank's CEO, MD, and different personnel with appreciate to a fee of offenses below Sections forty-six and forty-seven of the Banking and Regulation Act, 1949 at the side of the ones beneath neath Section a hundred and twenty B of the Indian Penal Code.
The petitions additionally sought to quash the crook grievance filed with the aid of using Reserve Bank of India in opposition to it beneath neath Section two hundred of the Criminal Procedure Code examine with Section forty-seven of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949. The gift petition changed into filed earlier than the Delhi High Court in May 2019 with the aid of using PNB. In it is a plea, PNB had invoked the inherent powers of the Court beneath neath Section 482 of CrPc to quash the order on the issuance of the system. By manner of background, the Reserve Bank of India had issued an exclusive round to banks on 'Cyber Security Controls Frauds' dated November 25, 2016. The round additionally counseled banks to discover Straight Through Processing among CBS and SWIFT messaging systems. It additionally spoke on exchange finance transactions and the misuse of SWIFT, a fund shifting interface, and despatched these records in a password-covered shape to Punjab National Bank.
Around January 29, 2018, the PNB alleged that fraud was dedicated and filed Fraud Monitoring Reports (FMR) and replace programs with the Reserve Bank of India, duly informing them that fraud to the music of Rs. 13,000 crore were detected at Brady House Branch of PNB. Following this, a display motive observes changed into despatched with the aid of using the RBI to PNB on August 23, 2018, asking them to reveal motive in writing as to why penalty beneath neath forty-seven A(1) (C) examine with Section forty-six (4) of the Banking Regulation Act 1949 ought to now no longer be imposed on PNB. RBI then filed a crook grievance beneath neath Section two hundred of the CrPC,1973 examine with phase forty-seven of the Banking Regulation Act 1949 earlier than Patiala House Metro Magistrate looking for the prosecution of PNB and its officers for a fee of offenses beneath neath Section forty six of Banking Regulation Act 1949 examine with Section a hundred and twenty B of Indian Penal Code,1860.
A listening to happened in relation to reveal motive observe on December 21, 2018, next to which the Committee of Executive Directors of RBI exceeded an order beneath neath Section 47A of Banking Regulation Act, implementing a penalty of Rs. 2 crores on PNB. Finally, on March 11, 2019, the Court of Metropolitan Magistrate of Patiala House Court, New Delhi exceeded an order in which PNB and others named in crook grievance with the aid of using RBI had been summoned to seem earlier than the Court. The identical changed into communicated to them at the side of a path to pay the penalty of Rs 2 crores inside 14 days of receiving the order. Disagreeing with the choice of the Patiala House District Court, Punjab National Bank moved the Delhi High Court in May 2019 for quashing of the crook grievance registered in opposition to it with the aid of using RBI and for placing apart of the order dated March 11, 2019.
In it is a petition filed through Shardul Amarchand Mangaldas & Co., the Punjab National Bank submitted earlier than the Court that during it is allegations, the RBI had no wherein indicated which sub-phase of Section forty-six of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 they had been relating to at the same time as summoning the bank's officers and personnel. It changed into additionally submitted that Section forty-six of the Act has an extensive-ranging scope. For instance, if Section forty-six (1) punishes someone who wilfully furnishes an assertion that's fake in any cloth particular, then Section forty-six (2) punishes whoever fails to provide any assertion beneath neath Section 35 (2) of the Act.
Similarly, Section 46 (4) punishes another violation of provisions of the Banking Regulation Act 1949. The punishments in every case vary as well. Thus, it changed into PNB's competition that because of this loss of identity of a specific sub-phase of forty-six, top-notch prejudice was brought on to it. It similarly contended that RBI's crook grievance and order dated March 11, 2019, of the Patiala House courtroom docket changed into ex facie unlawful and must be set apart as a result of one-sided averments.
In it is a petition, Punjab National Bank trusted numerous judgments of the Supreme Court inclusive of Sunil Bharti Mittal v CBI ( 2015) and Pepsi Foods Ltd. v Judicial Magistate (1998) to enunciate the precept that a summoning order ought to replicate due utility of thoughts and the Justice of the Peace have to offer enough foundation for intending in opposition to the accused. Senior Advocate Mahesh Jethmalani and suggest Mugdha Pande, representing RBI, adversarial the plea. The Court proceeded to brush aside the plea with the aid of using PNB. Punjab National Bank changed into represented with the aid of using Senior Advocate Dayan Krishnan and Nishant Joshi of Shardul Amarchand Mangal Das.
Document: