Latest Articles
Female Genital Mutilation- Violation of Human Rights

Female Genital Mutilation- Violation of Human Rights
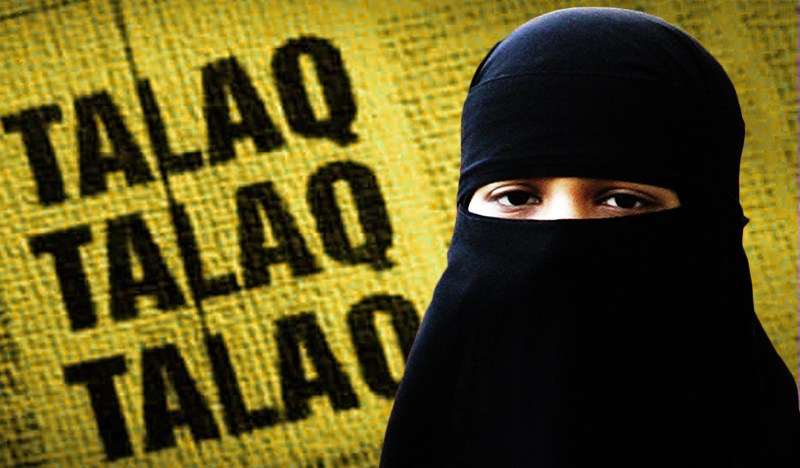
Female Genital Mutilation or FGM comprises of procedure involving partial or total removal of the external female genitalia or other injury to the female genital organs for non-medical reasons. It is usually targeted at women between 1-15 years. But it can also be sometimes seen in married or adult women.
Despite the global and national efforts to promote abandonment of the practice, FGM remains widespread in different parts of the world. Over 200 millions girls and women have undergone FGM. The practice is most common in 30 countries across Africa and in some countries in Asia and the Latin America and among migrants from these areas.
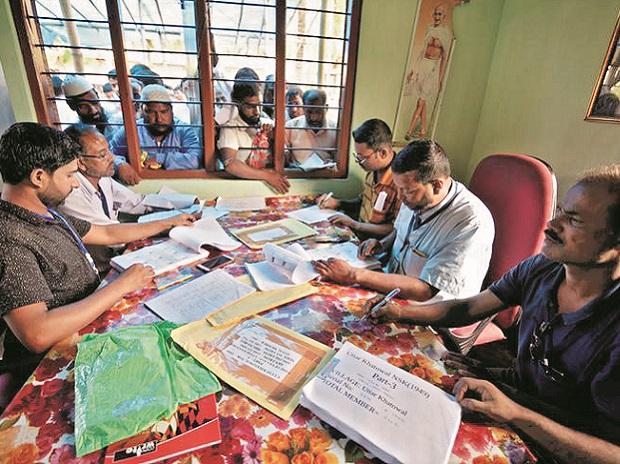
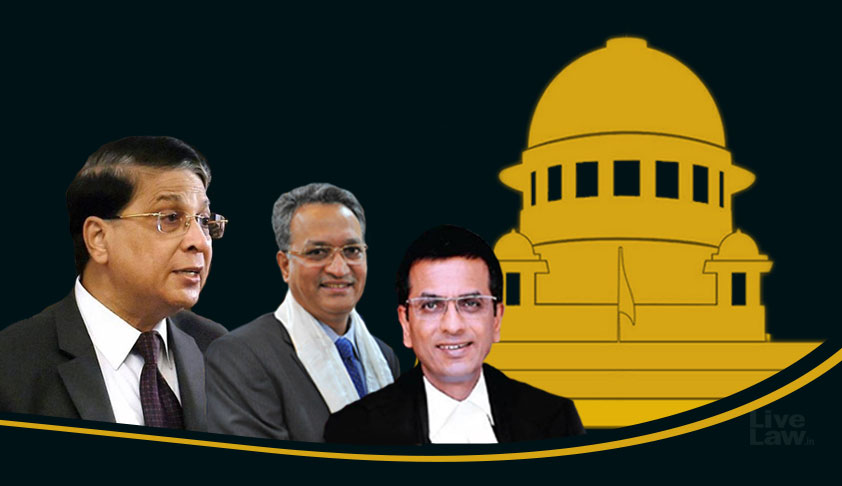
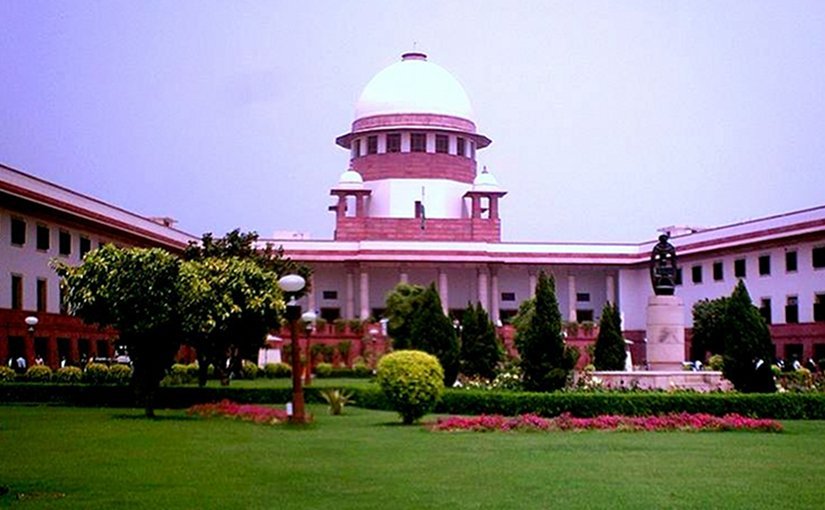
Female Genital Mutilation commonly known as FGM has been an eye opener for the Ministry of Women and Child Development recently and set the system in motion. The practice of FGM is uncontrollable in India from time immemorial. But this issue has seen the light of the day when human rights advocate raised this issue by filing a public interest litigation in Supreme Court for issuing the writ of Mandamus or any other direction to ban the practice of FGM in India.
Supreme Court looking at the severity and the concern considered various factors namely the female minors of Bohra community are being subjected to the practice of FMG also known as Khatna which is a process of removing part or all of the female genitalia are exposed to serious health issues thereby posing risks to their life. Though this practice is an offence under section 320, 322, 334, 335,336,337, 338 and 340 of Indian Penal Code, there is no specific laws for female genital mutilation. All the above mentioned laws are general ones and nothing in specific to FGM.
This practice is against the fundamental right of Article 14 and 21 of the Indian Constitution as the child who undergoes this practice is denied the equality status. Also they suffer the differential system of practice of Khatna upon them. This includes denial with the life and personal liberty. These are the basic fundamental rights which a citizen (including children) is entitled to enjoy.
The myth behind the practice of FGM is that Muslim men of Bohra community are mostly merchant and they need to travel a lot, so due to this absurd notion, wives of these men must not feel sexual urges when they are away, thereby the female of this community is subjected to the practice of Khatna so that their wives remain chaste. The fact that confuses is that Khatna is followed even when there is no mention of it in the Holy Quran.
Across the world the practice of Khatna is outlawed by many countries. Voices have been raised against this inhuman practice and for its ban in India. The Supreme Court considering the seriousness of this issue has accepted the PIL and passed the order in favour of Muslim females to ban the practice of Khatna and gave direction to the Government to make the law for the subject to specifically deal with it and declare the Khatna a serious criminal offence.
February 6 is declared is that International day of Zero Tolerance for Female Genital Mutilation. The United Nations have strives to destroy FGM completely by 2030. 13 countries have framed laws banning FGM.