Latest Articles
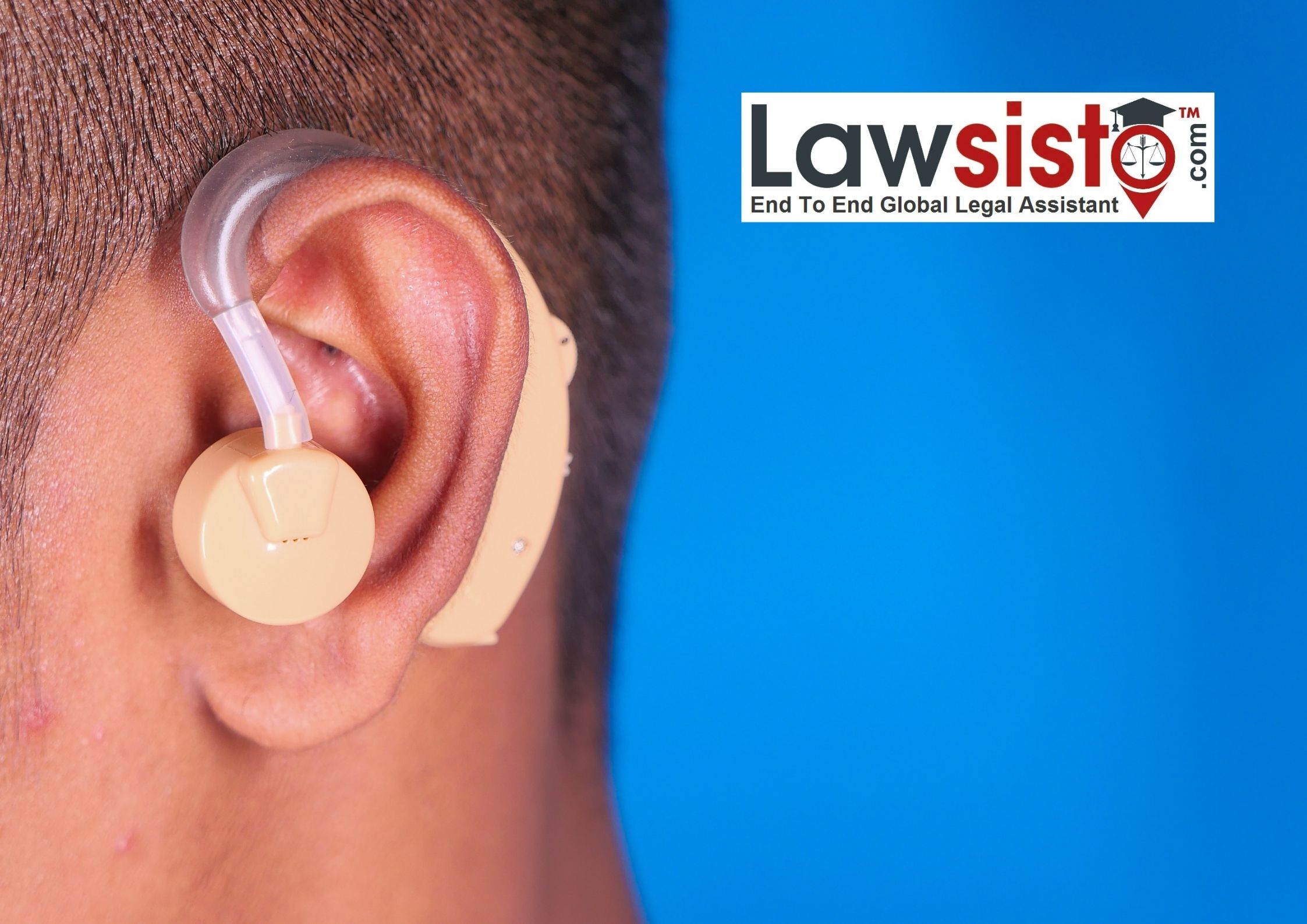
What rights do a disabled person in India have?

What rights do a disabled person in India have?
According to Section 2(s) of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016, “person with disability” means a person with long term physical, mental, intellectual or sensory impairment which, in interaction with barriers, hinders his full and effective participation in society equally with others. The UN General Assembly adopted the Convention on Rights of Persons with Disabilities on December 13th, 2006.
As per the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016, the government shall ensure that the disable persons enjoy the right to equality and life with dignity. The government should also take appropriate steps to utilise the capacity of such persons by providing an appropriate environment. The persons have the right to not be discriminated and deprive personal liberty on the ground of disability. The act also protects disabled women and children to enjoy rights equally with others.
The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016, also provides the Right to Community Life, protection from cruelty and inhuman treatment and protection from abuse, violence and exploitation.
Anyone who believes that an act of abuse, violence or exploitation has been or is being is likely to be committed against a disabled person may give information about it to the Executive Magistrate within the local limits of whose jurisdiction such incidents occur. The Executive Magistrate can stop or rescue the disable person or provide protection or provide maintenance according to the circumstances.
There are also other benefits for the disabled persons under this Act such as reservation which has been increased from 3% to 4%. In government organization, 3-4% of vacancies will be filed with disabled persons. Government shall also provide reasonabe accomation and a conducive envionment to employees with disablement. Person wth disability shall not be denied of promotion. If an employee after being disable is not suitable for a particular post, then he shall be shifted to some other post with same pay scale and service benefits. If an employee is not suitable for any post, then he may be kept on a supernumerary post until a suitable post is available or until he attains the age of superannuation, whichever is earlier. The Government make necessary insurance schemes for their disabled employees(Article 26).
Disabled persons will have special courts and free education from the age of 6-18. Also the Government and local authorities shall ensure that education to blind and deaf is provided in the appropriate means and modes of communication. All government institutions of higher education and other higher education institutions receiving aid from Government should reserve 5% seats for persons with benchmark disabilities.
The Government in consultation with the Chief Commissioner or State Commissioner may conduct. encourage or support awareness campaigns to ensure that the rights under this Act is protected.
The Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016, was made keeping in view the principles of UN conference 2006. This is because India is signed as a signatory of the Conference on the rights of people with disabilities of the United Nations General Assembly. The 2016 Act protects the disabled persons from various forms of discrimination, increases their effective participation and inclusion in the society and ensures equality of opportunity and adequate accessibility.