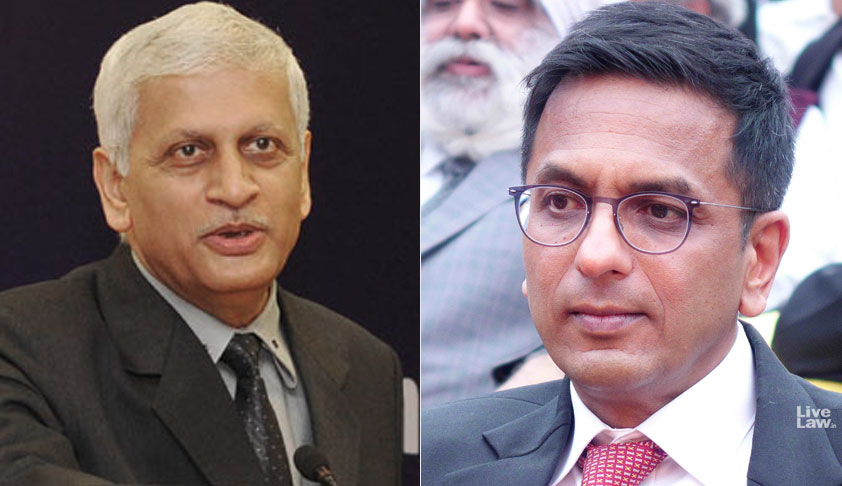
Latest Articles
OLD STATUTES MAKING A COMEBACK AMID VIRUS OUTBREAK

List of statutes which are being implemented by the Government of India
- Disaster Management Act, 2005
- Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897
- The Essential Services Maintenance Act, 1968
- Essential Commodities Act, 1955
How are these statutes being utilised amid COVID- 19?
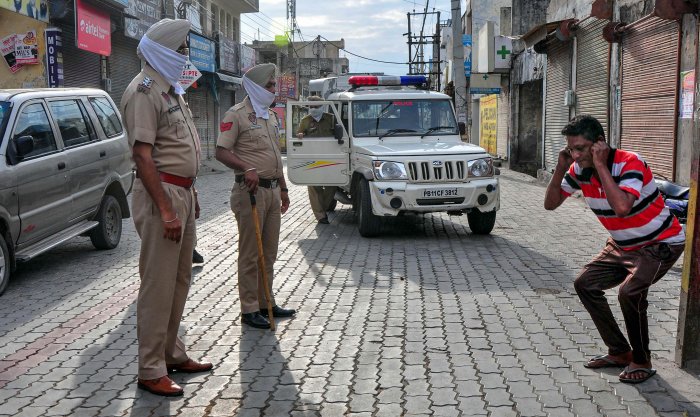
All these acts are being utilised in different senses in order to regulate the flow of essential goods, inter-state trade and for the classification of this kind of disaster. Section 6 (2) (i) of the Disaster Management Act, 2005 was invoked by the Government of India amid the outbreak of COVID-19. The measures laid down was with the primary purpose of restriction on residents from moving outside of their homes. The government issued orders for the closure of all offices, factories and shops. Only essential commodities will still be available.
The present pandemic is being classified as a disaster under section 2(d) of DMA, 2005. Even though diseases aren't worded under the act. Yet its implications are imposed by the government through interpretation. The central government is given wide powers under this Act. Section 72 of the DMA, 2005 established the overriding effect of the provisions under this act over all other laws.
The ESMA was invoked as a result of incidents of attacks on doctors in Delhi. The doctors went on a countrywide strike. Thus, the Delhi government implemented the provisions under ESMA in order to prevent further strike amid an already horrifying pandemic. Other states also implemented similar acts in order to control the situation. Rajasthan implemented the Rajasthan Essential Services Maintenance Act, 1970. Even Telangana had to implement something similar while Maharashtra invoked the provisions of Maharashtra Essential Services Maintenance Act which was enacted in 2017
Section 3 of the ESMA provides for punishment to any person violating regulations under this Act. It utilizes Section 188 of the Indian Penal Code for the same. Maharashtra invoked the Epidemic Diseases Act in order to close down corporate offices and impose a fine for spitting in public in major cities of the state.
The Epidemic Diseases Act, 1897 is about 123 years old. This Act is one of the oldest amongst the others. This act was charted in order to control the panic and spread of the bubonic plague which took place in Bombay. Its purpose is to prevent the proliferation of epidemics and such deadly diseases through community spread. Special powers are conferred to the Central Government. The local authorities are also required to implement precautionary measures to contain the upsurge and spread of epidemic diseases.
Essential Commodities Act, 1955 is being utilized to check the price of essential commodities in order to prevent hoarding. The provisions of this act are schemed to ensure the easy availability of essential commodities and to protect consumers from dishonest and unethical vendors. For example- major commodities like food items like edible oil and seeds, pulses, rice, petroleum and petroleum products etc are covered. Even Sanitary napkins for women are rightly included as an essential commodity.