Latest Articles
DEMOCRACY IN INDIA

DEMOCRACY IN INDIA
Democracy in its simple sense means government by the people, which means a form of government in which people have the supreme power and are exercised directly by them or by their elected agents. This is done under a free electoral system.
Democracy is also known as “rule of the majority”. In the case of democracy power can’t be inherited. Citizens themselves elect their leaders from the representatives wh stand in an election. The representative with the majority of votes gets elected.
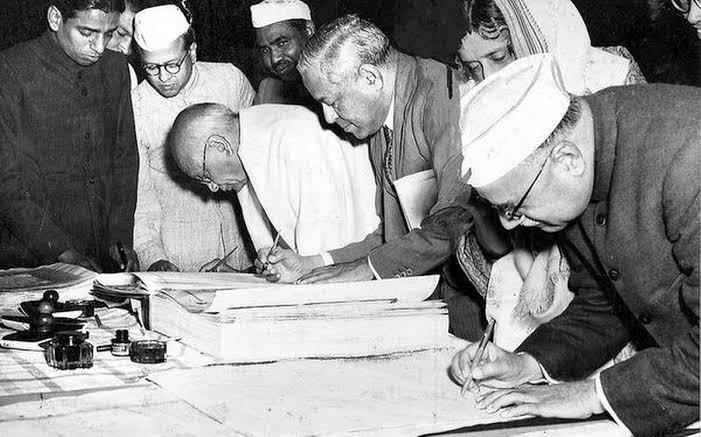
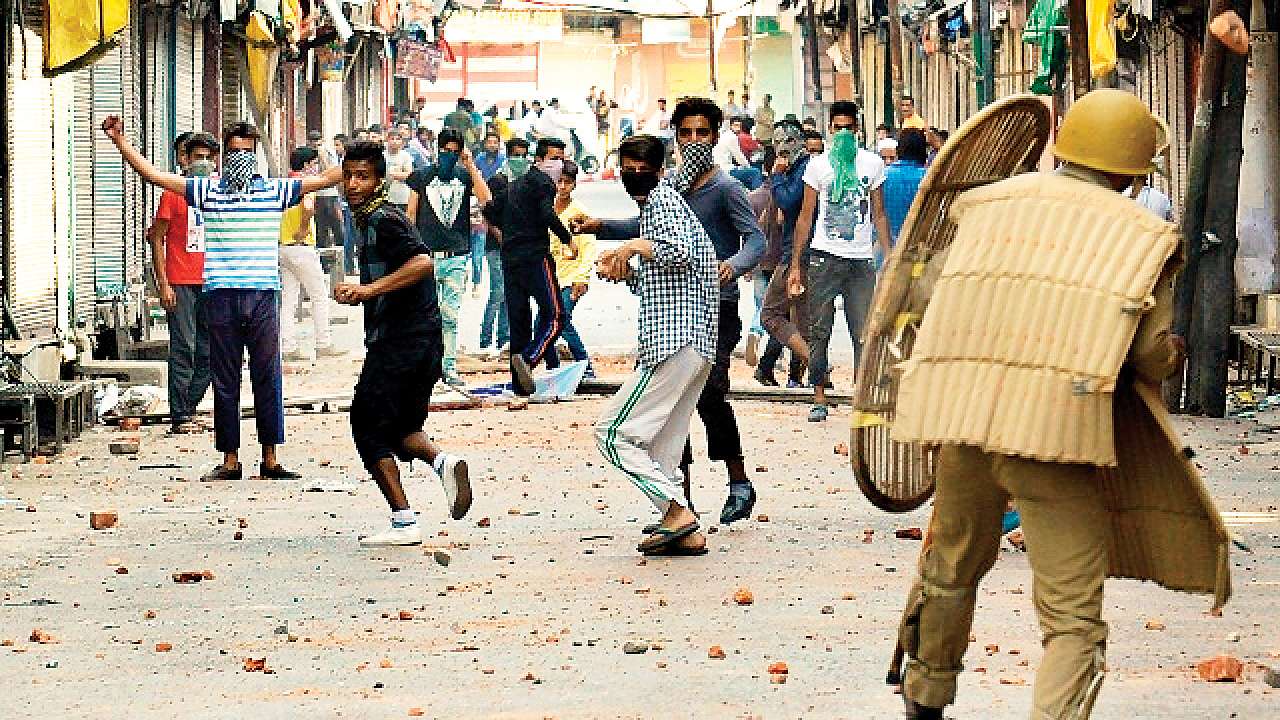
India is the world’s largest democracy. After its independence in 1947, India became a democratic country. After the independence, the citizens of India were given the right to vote in order to elect their leaders. In India, it gives its citizens the right to vote without any discrmination based on caste, color, creed, religion, and gender.
India has five democratic principles –
- Sovereign- Sovereign means that the State has independent authority. This means that the State has the power to legislate on any subject. Also that it is not subject to the control of any other State or external power.
- Socialist- The term Socialist was added by the 42nd Amendment in 1976. Before that the Constitution had socialist content in the form of Directive Principles of State Policy (Part IV of the Indian Constitution). The word socialist used here refers to democratic socialism. This means achievement of socialist goals through democratic, evolutionary and non-violent means. Essentially, it means that the wealth should be shared equally by society through distributive justice, that it should not be concentrated in the hands of few. Also that the government should regulate the ownership of land and industry to reduce socio-economic inequalities.
- Secular- The term Secular was also added in the Preamble by the 42nd Amendment in 1976. Secular means that the constitution and law determines the relationship between the government and religious groups. It separates the power of the state and religion. There is no difference of religion i.e. Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Sikhism, Christianity and Islam are equally respected. This means that there is no state religion. All the citizens of India are allowed to profess, practice and propagate the religion they wish.
- Democratic- The people of India elect their governments by a system of universal adult franchise. It is popularly known as "one person one vote". Every citizen of India who are 18 years of age or older and not otherwise debarred by law is entitled to vote. The word democratic refers not only to political democracy but also to social and economic democracy.
- Republic- This word denotes a government where no one holds public power as proprietary right. The head of state is elected and not a hereditary monarch.
There are two types of democracy:-
- Direct Democracy- Direct Democracy is where the head of the State is directly elected by the people.
- Indirect Democracy- Indirect democracy is where the peoples’ representatives elect the head of the State.
In India we follow indirect democracy. In the Central level, the peoples’ representatives are elected as members of Parliament who in turn elect the Prime Minister. In the State level, the members of legislative assembly are elected by the people who in turn elect the Chief Minister.